When paper is the solution, it cannot become plastic again.
Natural Coating for Paper Packaging
A Sustainable Solution for the Future
Reading time: 7 min.
White Paper Abstract
Embracing the Industrial Bioeconomic Revolution

The global packaging industry is a major contributor to micro plastic pollution. In 2020, 368 million tonnes of plastic packaging have been produced, of which only 9% has been recycled. Efforts to reduce plastic waste are ongoing and include recycling, bans on single-use plastics (as Single-Use Plastics SUP European directive), and promoting the use of alternative materials.
The use of coated paper to reduce plastic pollution is an innovative approach to addressing the environmental impact of traditional plastic materials and a transition from plastic packaging to paper coating is already occurring. Nevertheless, the coating of paper with polymers is necessary to make it resistant to water, oil, grease, oxygen, and other substances. However, the market is ready and willing to introduce biobased and natural based coating as alternative to the still widely used plastic coating technologies.
In this white paper we will present how Lamberti has developed an innovative solution of this industry (Esacote BIO BC 100), 100% natural water based dispersion for paper coating using a vegetable by-product from the food industries. This new product combines outstanding barrier properties to water along with grease and oil resistance. Being a 100% bio based dispersion of a chemically unmodified natural substance it can fulfil perfectly the most stringent environmental and technical demands of the current market.
Advancements in Barrier Coating technologies in the Food Packaging
Maintaining food quality, by hindering oxygen and moisture diffusion and minimizing waste are hallmarks of
effective food packagings.
There are several technologies in use to impart barrier and/or thermo sealing properties to paper. We explore
various coating methods critically evaluating their environmental impact and recyclability:
- Metallization
- Fossil Based Coating
- Bio-based coatings
- Extrusion Coating
- Hybrid coatings
- PFAS
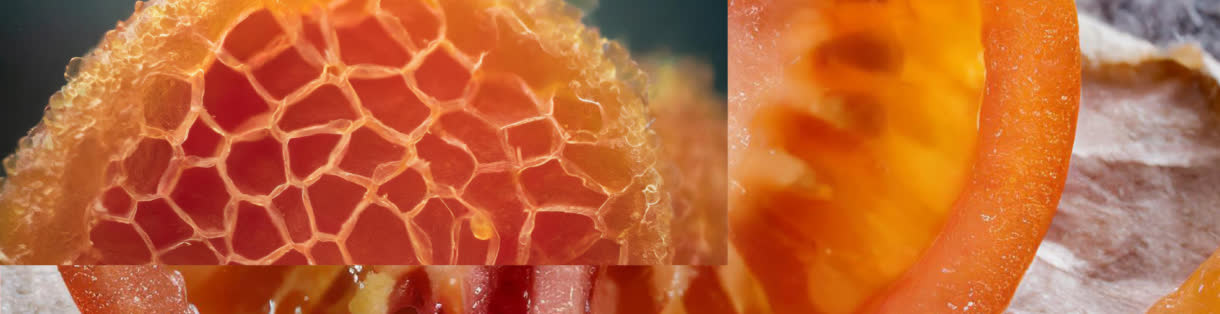
Biomimicry: Nature’s Blueprint for Sustainable Barrier Materials
Lamberti draws inspiration from nature's ingenious design principles in the pursuit of advanced barrier materials.
Over millennia, evolution has crafted optimal solutions, providing invaluable insights for developing sustainable innovations. This section delves into the biomimetic approach, drawing inspiration from the remarkable barrier properties of plant cuticles, which can effectively contribute to a sustainable future in food packaging.
Composed primarily of the biopolymer cutin, plant cuticles shield fruits, leaves, and stems from environmental threats. Recognizing the potential of this intricate natural barrier, our aim was to translate its functionalities into practical solutions for the packaging industry.
Results at a glance
By harnessing the power of biomimicry and utilizing sustainable resources like tomato peels, Cutin based dispersion technology represents a paradigm shift in barrier coating.
- Water holdout: Unlike other biobased materials, Cutin Dispersion achieves water resistance comparable to synthetic polymers, addressing a longstanding limitation.
- Oil & grease protection: It maintains excellent oil & grease resistance, on par with biobased options, ensuring product integrity.
- Heat sealability: Its superior sealing capabilities facilitate efficient conversion within existing packaging lines.
- MOSH/MOAH barrier: The low HVTR signifies a robust barrier against these potentially harmfulsubstances, enhancing food safety.
- Level of customization like natural colour and typical aroma
- Sustainability at its core: Utilizing a readily available by-product of the food industry aligns with circular economy principles, minimizing waste and environmental impact.

White Paper

